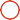
The working condition of the trackless transfer carts refers to its working environment and conditions in practical applications. Understanding these conditions is essential for selecting the right type of trolley. The following is a typical use scenario analysis of trackless cart:
![]()
1. Ground conditions
Flat ground: Most trackless transport vehicles are suitable for running on flat ground, such as concrete, asphalt paved factory floor and warehouse floor.
Uneven ground: Some models of trackless transport vehicles can be used on slightly uneven ground, such as construction sites, docks, etc., but the ground slope and obstacles should be within the tolerance range of the vehicle.
2. Ambient temperature
Normal temperature environment: The transfer trolley is usually suitable for indoor and outdoor normal temperature environment, the temperature range is generally between -10°C and 40°C.
Special temperature environment: When used in a high or low temperature environment, it is necessary to select vehicles that adapt to specific temperature conditions or carry out corresponding technical modifications to the vehicle.For example, under high temperature conditions, we need to explosion-proof the motor battery.
3. Load and type of cargo
Heavy load: Depending on the model, the carrying capacity of the transfer trolley can range from a few tons to dozens of tons, which is suitable for handling heavy equipment, materials and bulk cargo.
Specific cargo types, such as steel coils, molds, cable reels, etc., need to be configured with specific supports and fixing devices to ensure stability and safety during transportation.
4. Operating space
Spacious space: In the factory workshop or warehouse, there is usually enough operating space, and the railless transfer vehicle can move freely to complete the handling of large goods.
Small space: In narrow channels or conditions requiring precise positioning, the railless transfer vehicle is required to have good steering ability and flexibility, and some models also support rotation in place.
5. Running distance
Short distance handling: Usually in a factory or warehouse to carry out short distance handling tasks.
Long-distance handling: In some larger industrial parks or port terminals, railless transfer vehicles may need to carry out long-distance material transfer, and battery life and charging convenience need to be considered.
6. Operation frequency
High frequency operation: In the case of frequent material handling, such as the transfer from the end of the production line to the warehouse, this condition has high requirements for the durability and battery life of the equipment.
Low frequency operation: In some cases of intermittent use, the frequency of use of the vehicle is low, and the battery life and maintenance needs are relatively small.
![]()
7. Operating environment
Indoor environments, such as factory workshops and warehouses, usually have better lighting and fewer environmental disturbances.
Outdoor environment: such as ports, construction sites, etc., need to consider the weather factors, such as rain, snow, wind and sand, etc., on the vehicle performance and operation safety.